Що таке багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA)?
1. Що таке багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA)?
Багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA, 3FA) додає додатковий рівень безпеки, щоб підтвердити, що вхід виконуєте саме ви. Окрім пароля, система попросить вас ввести одноразовий код із MFA застосунка, чат-бота, push-сповіщення, SMS або електронної пошти. Або ж потрібно буде відповісти на секретне запитання, використати відбиток пальця чи розпізнавання обличчя.
Багатофакторна автентифікація надійно захищає ваш обліковий запис від кібератак і випадків, коли пароль може потрапити не в ті руки. Вона допомагає запобігти фішингу, атакам «людина посередині», підбору паролів та іншим загрозам.
Багатофакторну автентифікацію також називають двофакторною (2FA) або автентифікацією у два етапи. Це тому, що найчастіше для зручності користувачів під час входу використовують комбінацію з двох факторів автентифікації.
2. Фактори багатофакторної автентифікації
Багатофакторна автентифікація підвищує безпеку, оскільки поєднує різні за природою фактори автентифікації.
Наразі виділяють три основні типи факторів автентифікації:
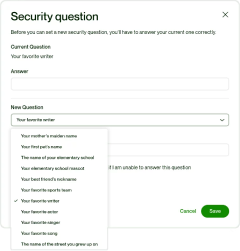
- Те, що ви знаєте: паролі, логіни або відповіді на секретні запитання, наприклад, ім’я вашого кота чи улюблений автор.
- Те, що у вас є: одноразовий код, згенерований на вашому смартфоні через MFA-застосунок або отриманий через SMS, чат-бот у месенджері чи електронну пошту. Це також може бути спеціальний пристрій для генерації одноразових паролів — апаратний OTP-токен. Він нагадує брелок, USB-накопичувач, картку або калькулятор з маленьким екраном на 6 чи 8 цифр.
- Те, чим ви є: біометричні дані, такі як відбитки пальців або сканування сітківки ока, а також розпізнавання обличчя.
Деякі фахівці з безпеки називають можливий четвертий фактор - середовище користувача. Проте досі тривають дискусії щодо того, чи доцільно вважати середовище користувача окремим фактором. Тим не менше, в рамках багатофакторної автентифікації можна виділити два додаткові фактори:
- Перевірка місцезнаходження: Аутентифікація на основі місцезнаходження підтверджує особу користувача, враховуючи його географічне розташування. Наприклад, якщо обліковий запис, зареєстрований в одній країні, намагається увійти з іншого місця, система, використовуючи географічні та IP-фільтри, обмежить доступ до облікового запису.
- Аутентифікація, що базується на часі: Цей фактор перевіряє особу користувача, аналізуючи час спроби доступу в систему. Він ґрунтується на припущенні, що певні дії, наприклад, вхід на робочий комп’ютер, зазвичай відбуваються в передбачувані часові проміжки. Якщо спроба доступу відрізняється від очікуваного часу, система відмовить у доступі до облікового запису.
3. Як працює багатофакторна автентифікація
Вхід в обліковий запис тільки з іменем користувача та паролем здається простим, але це дозволяє будь-кому, хто має ці дані, отримати доступ до вашого акаунта з будь-якої точки світу. Саме тут на допомогу приходить багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA), яка додає додатковий рівень захисту.
Успіх багатофакторної автентифікації полягає в стратегічному поєднанні різних факторів автентифікації, кожен з яких компенсує слабкості іншого. Це ускладнює життя зловмисникам, адже одночасне компрометування всіх факторів за обмежений час є складним завданням. Навіть якщо один фактор буде скомпрометовано, обліковий запис залишатиметься захищеним.
Коли увімкнено багатофакторну автентифікацію, процес автентифікації стає більш складним.
- Перший крок — це звичайний процес введення імені користувача та пароля (те, що ви знаєте).
- Далі ви проходите через другий фактор — унікальний етап перевірки особи, яким може бути:
- Те, що у вас є: одноразовий код, згенерований на вашому смартфоні через MFA-додаток або отриманий через SMS тощо.
- Те, чим ви є: відбиток пальця або розпізнавання обличчя.
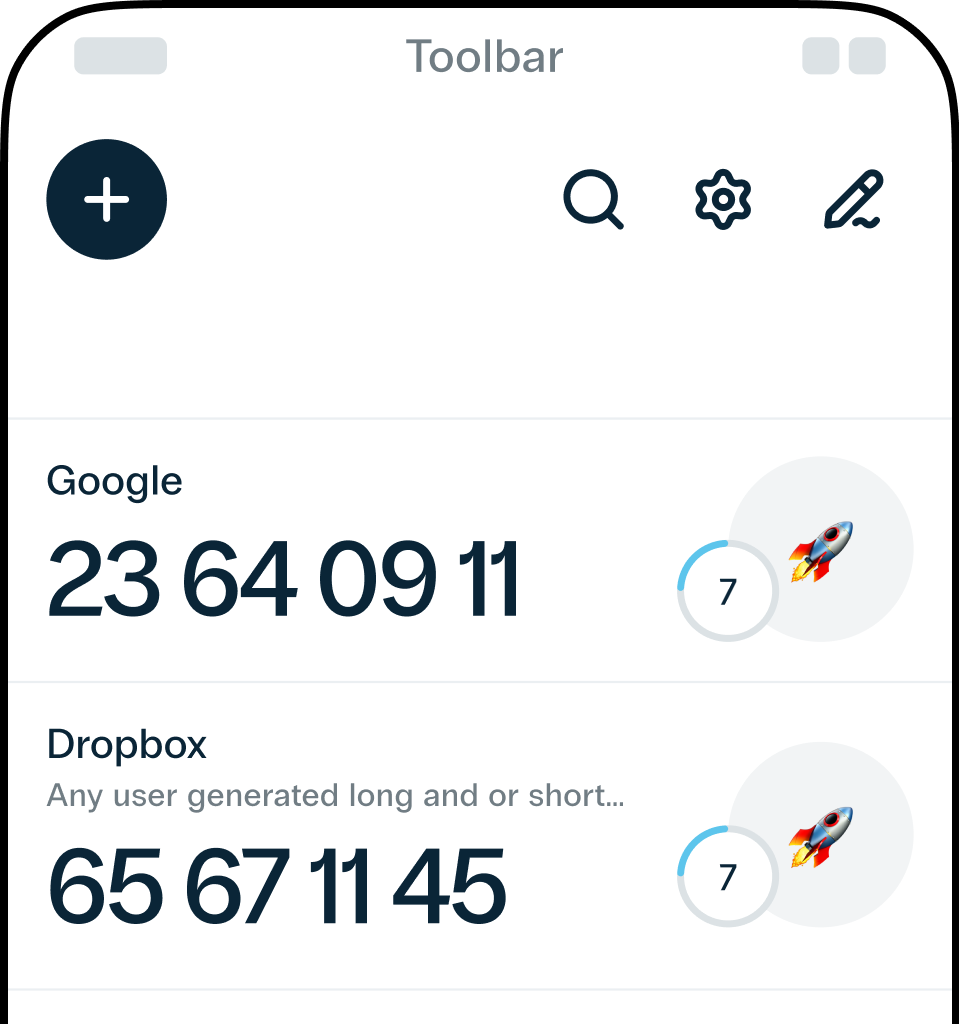
Припустимо, ви вибрали застосунок для генеації одноразових паролів Protectimus Smart як другий фактор. Відкривши застосунок на смартфоні, ви побачите 6-значний код, який генерується в реальному часі. Введення цього коду на сайті надає вам доступ.
Якщо хтось спробує увійти під вашим ім’ям, вони зіштовхнуться з перешкодою. Навіть знаючи ваш логін і пароль, вони застрягнуть на другому факторі. Без вашого смартфона вони не зможуть отримати змінюваний 6-значний код. Цей код оновлюється кожні 30 секунд, що гарантує безпеку, навіть якщо вони дізнаються вчорашній код.
Розбір процесу багатофакторної автентифікації:
- Реєстрація: користувачі створюють обліковий запис, задаючи логін і пароль, а також додають додаткові елементи, як-от токен на смартфоні, апаратний токен або віртуальні дані, такі як електронна пошта чи номер телефону. Для підвищення безпеки можна також додати біометричні дані, наприклад, відбитки пальців.
- Автентифікація: користувачі з увімкненою багатофакторною автентифікацією при вході на сайт вводять свій логін і пароль (перший фактор), а потім отримують запит на введення одноразового коду або виконання інших дій за допомогою свого MFA-пристрою (другий фактор).
- Реакція: Користувачі завершують аутентифікацію, вводячи одноразовий код, натискаючи кнопку на апаратному токені, скануючи відбиток пальця або натискаючи на push-сповіщення.
4. Значення багатофакторної автентифікації
У міру того, як організації переходять у цифрову еру і беруть на себе більшу відповідальність за захист даних клієнтів, стає очевидною необхідність у надійних заходах безпеки, включаючи впровадження багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA).
Покладатися лише на логіни та паролі — це ненадійно і вразливо для зловмисників. Користувачі часто мають труднощі з грамотним управлінням своїми обліковими даними, що робить їх вразливими до хакерських атак.
MFA — це нобхідне рішення, яке додає додатковий рівень перевірки до онлайн-акаунтів і знижує ризик несанкціонованого доступу через скомпрометовані паролі. Багатофакторна автентифікація захищає акаунти від фішингу, атак «людина посередині», підбору паролів, атак типу «stuffing» на основі облікових даних, клавіатурних шпигунів та інших атак, пов’язаних з паролями.
Сертифікації та вимоги до відповідності індустріальним та міжнародним безпековим стандартам підкреслюють важливість багатофакторної автентифікації. Вона є ключовим елементом для дотримання суворих стандартів, таких як PCI-DSS, PSD2, GDPR, NIST, FFIEC, NYDFS, NAIC та інших норм безпеки. Для компаній і організацій, які працюють з конфіденційними даними, фінансовими транзакціями чи особистою інформацією користувачів, впровадження MFA є особливо важливим.
MFA зміцнює кібербезпеку, відповідає галузевим стандартам і забезпечує надійний захист від еволюціонуючих кіберзагроз. Вона є незамінним компонентом у постійній боротьбі з цифровими ризиками.
5. Від яких загроз захищає багатофакторна автентифікація
Багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA) є потужним захистом, що охороняє облікові записи користувачів від різних кіберзагроз. Вона захищає від брутфорсу, фішингу, атак «людина посередині», підбору паролів, викрадення сеансів, соціальної інженерії, атак через словники, кейлогерів і інших загроз, пов'язаних з перехопленням паролів.
Фішинг
MFA відіграє ключову роль у захисті від атак фішингу, коли хакери вводять користувачів в оману, змушуючи їх розкривати облікові дані через шахрайські електронні листи або підроблені вебсайти. Вимога другого етапу автентифікації додає додатковий рівень захисту, знижуючи ефективність фішингових схем.
Брутфорс
MFA допомагає протидіяти ризику брутфорс-атак, коли хакери систематично намагаються підібрати паролі, пробуючи безліч комбінацій. Додатковий фактор автентифікації значно ускладнює задачу зловмисникам, навіть якщо їм вдається розшифрувати пароль.
Використання кейлогерів
MFA захищає від атак за допомогою кейлогерів - шпигунів-клавіатур, коли шкідливе програмне забезпечення записує натискання клавіш для отримання чутливої інформації, такої як паролі. Додавши додатковий рівень автентифікації, наприклад, одноразовий код або біометрію, стає значно важче використовувати шпигунів для повного доступу до облікових записів користувачів.
Використання крадених облікових даних
MFA перешкоджає атакам з використанням крадених облікових даних, коли хакери застосовують витіклі пари логінів та паролів для несанкціонованого доступу. Додатковий етап автентифікації робить крадені облікові дані недостатніми, посилюючи захист цифрових систем від автоматизованих спроб входу.
Перехоплення сеансу
MFA захищає від перехоплення сеансу — атаки, коли хакери викрадають активний сеанс користувача для несанкціонованого доступу. Навіть якщо зловмисник отримає дані сеансу, додатковий етап автентифікації додає ще один рівень захисту, що ускладнює успішний доступ до акаунта.
Соціальна інженерія
MFA служить захистом від атак соціальної інженерії, коли зловмисники маніпулюють людьми, аби ті розкрили конфіденційну інформацію. Навіть якщо хакер вмовить користувача поділитися обліковими даними, додатковий етап автентифікації створює ще один бар'єр для несанкціонованого доступу.
Атаки типу "Людина посередині"
MFA допомагає запобігти атакам типу "Людина посередині" (Man-in-the-Middle, MitM), коли зловмисники перехоплюють і маніпулюють комунікацією для отримання доступу до чутливої інформації. Додаткові етапи перевірки, особливо при використанні функції CWYS (Confirm What You See) для підпису даних, ускладнюють зловмисникам маніпулювання або перехоплення процесу автентифікації.
Скомпрометовані паролі
Паролі становлять ризик, коли потрапляють до неавторизованих осіб. Наприклад, якщо користувач записує свій пароль на папері, він може бути вкрадений, що дозволяє отримати доступ до акаунта. З іншого боку, 2FA підвищує безпеку, вимагаючи підтвердження з іншого пристрою після введення пароля.
6. Приклади багатофакторної автентифікації
Дізнайтеся, як бізнеси використовують багатофакторну автентифікацію (MFA) у реальних ситуаціях. Ми розглянемо практичні приклади, які демонструють, як організації з різних галузей успішно впроваджують MFA:
Різні правила безпеки для груп користувачів у Volet
Volet використовує MFA для налаштування безпеки для різних груп користувачів. Співробітники можуть використовувати лише апаратні OTP токени, а також для них налаштовані географічні та IP-фільтри. Водночас кінцеві користувачі мають більше вибору, обираючи між апаратними OTP токенами, 2FA-застосунками або чат-ботами в месенджерах. Додатково, транзакції кінцевих користувачів захищені завдяки функції підпису даних CWYS (Confirm What You See).
Корпоративна безпека в Xchanging Italy
Xchanging Italy, частина DXC Technology, використовує рішення багатофакторної автентифікації Protectimus для захисту доступу до більшості корпоративного програмного забезпечення. Це рішення було обрано для забезпечення ефективного захисту всіх сервісів, щоб уникнути складнощів із інтеграцією 2FA в кожну програму окремо. Рішення Protectimus Dynamic Strong Password Authentication (DSPA) бездоганно інтегрується з Active Directory, перетворюючи паролі користувачів на динамічні двофакторні паролі. Вони поєднують звичайний пароль з тимчасовим одноразовим паролем, що генерується на основі часу (TOTP). Це дає змогу забезпечити надійний захист усіх підключених сервісів без необхідності встановлювати додаткове програмне забезпечення на комп’ютерах співробітників.
Захист доступу до VPN та email в SICIM
SICIM використовує двофакторну автентифікацію для посилення безпеки доступу до корпоративного VPN. Окрім цього, вони додали 2FA для додаткового захисту до електронних поштових скриньок співробітників, забезпечуючи більшу безпеку для чутливої інформації.
7. Методи багатофакторної автентифікації
Багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA) значно підвищує цифрову безпеку, вимагаючи від користувачів підтвердження своєї особи за допомогою різних методів. Існує кілька підходів, кожен з яких по-своєму зміцнює процес автентифікації. Далі ми поділимо ці методи на групи, щоб детальніше розглянути їхні особливості та способи використання.
Автентифікація на основі знань
Паролі: Незважаючи на свою простоту, паролі часто використовуються в рішеннях MFA як перший етап багатофакторної автентифікації.
Секретні запитання: Традиційні секретні запитання поступово втрачають популярність через повторюваність введення даних. Динамічні запитання, що базуються на реальних даних, є більш безпечним та зручним варіантом.
Аппаратні OTP-токени
Класичні апаратні OTP-токени: Фізичні пристрої у вигляді брелоків або карток з дисплеєм і кнопкою, що генерують 6- або 8-значні одноразові коди. Класичні апаратні токени мають жорстко закодовані секретні ключі, які користувач не може змінити.
Програмовані апаратні OTP-токени: Фізичні пристрої у вигляді брелоків або карток, що генерують одноразові коди для двофакторної автентифікації. Ключова перевага апаратних токенів з можливістю програмування — можливість змінювати секретний ключ. Це зручно для бізнесу, адже дозволяє оновлювати ключі за потреби, підвищуючи рівень безпеки та усуваючи ризики, пов’язані з передачею ключів.
Стандарт U2F: Використовує USB- або NFC-токени разом із додатками, що підтримують відкритий стандарт U2F. Стандарт U2F дозволяє легко налаштувати додатковий фактор автентифікації на сумісних платформах.

SMS-автентифікація
Одноразовий пароль для підтвердження особи надходить у SMS повідомленні на довірений номер. Попри зручність, SMS автентифікація менш безпечна, оскільки зловмисники можуть перехопити повідомлення або отримати доступ до номера через заміну SIM-карти.
Застосунки для двофакторної автентифікації
Мобільні застосунки для 2FA, такі як Protectimus SMART чи Google Authenticator, генерують одноразові паролі (OTP), забезпечуючи надійну альтернативу SMS-автентифікації.
Автентифікація через чат-боти в месенджерах
Інноваційний метод двофакторної автентифікації використовує MFA чат-ботів в популярних месенджерах, таких як Facebook Messenger, Telegram і Viber, для доставки одноразових паролів (OTP). Цей підхід вирішує кілька важливих проблем: він забезпечує вищий рівень безпеки порівняно з SMS-автентифікацією, є абсолютно безкоштовним і простим у використанні як для клієнтів, так і для їхніх користувачів.
Push-сповіщення для 2FA
Push-сповіщення для двофакторної автентифікації підвищують безпеку та зручність MFA, замінюючи коди доступу на сповіщення. Цей метод ефективно бореться з фішингом, але вимагає доступу до певних даних на мобільних пристроях.
Email-автентифікація
Аутентифікація через електронну пошту працює подібно до SMS-токенів, але коди надсилаються на електронну пошту. Це резервний метод для користувачів, які не мають доступу до своїх телефонів, який забезпечує зручність і збереження безпеки.
Біометрична автентифікація
Біометрична аутентифікація використовує унікальні характеристики, такі як відбитки пальців або риси обличчя. Це безпечний і зручний метод MFA, однак не всі пристрої підтримують цю технологію.
Аутентифікація на основі місцезнаходження та часу
Методи аутентифікації на основі місцезнаходження та часу, зазвичай використовуються у поєднанні з іншими методами аутентифікації і додають додатковий рівень безпеки:
- Географічні фільтри обмежують доступ до акаунтів, дозволяючи вхід лише з вибраних країн.
- Фільтрація IP-адрес забезпечує доступ до акаунтів лише з вказаних IP-адрес.
- Часові фільтри надають доступ до акаунтів тільки в межах визначених робочих годин.
Ці методи багатофакторної автентифікації забезпечують багаторівневий захист від несанкціонованого доступу, враховуючи різні потреби користувачів та питання безпеки. Організації можуть вибирати комбінацію методів, яка найкраще відповідає їх вимогам до безпеки та зручності використання.
8. Впровадження багатофакторної автентифікації в організаціях
Впровадження багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA) в організаціях вимагає дотримання основних практик для забезпечення максимальної безпеки:
- Пріоритет для важливих облікових записів: Почніть із захисту критичних облікових записів, таких як акаунти керівників та адміністраторів мережі, враховуючи юридичні вимоги та ефективність операцій.
- Вибір практичного рішення для MFA: Оберіть універсальне рішення двофакторної автентифікації, яке підтримує різні методи доставки одноразових паролів. Враховуйте такі фактори, як вартість, зручність, адаптивність, простота використання та інтеграції.
- Вибір надійного постачальника MFA: Для успіху важливо вибрати постачальника багатофакторної автентифікації, який відповідає вашим вимогам, легко інтегрується, стабільний та готовий допомогти з інтеграцією. Можливість інтеграції в існуючі ІТ-системи є важливою.
- Навчання користувачів: Чітко поясніть кінцевим користувачам важливість MFA. Для співробітників підкресліть, як це впливає на ефективність і прибутки компанії. Для клієнтів зробіть MFA максимально зручним і подумайте про можливі бонуси за добровільну активацію MFA.
Не забувайте, що MFA є важливим інструментом для захисту корпоративних і особистих даних. Розуміння переваг двофакторної автентифікації допомагає організаціям приймати обґрунтовані рішення та швидко впроваджувати ефективні засоби безпеки.
Дізнайтеся більше про цю тему в статті "5 кроків для підготовки вашого бізнесу до багатофакторної автентифікації".
9. Які галузі використовують багатофакторну автентифікацію
Від фінансового сектора до охорони здоров'я, освіти, онлайн-ігор, технологічного сектора, державних установ і енергетичної галузі, багатофакторна автентифікація стає важливою лінією оборони від несанкціонованого доступу та потенційних загроз безпеці. Давайте розглянемо, як MFA застосовується та які переваги вона приносить у різних галузях.
Фінансові послуги
У фінансовому секторі багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA) є важливою технологією захисту від несанкціонованого доступу. Впровадження 2FA, особливо з функцією підписання даних, як-от Confirm What You See (CWYS), забезпечує надійний захист доступу і транзакцій. MFA охороняє облікові записи користувачів і фінансові транзакції від фішингових атак, загроз типу "Man-in-the-Middle" (MITM) та спроб підміни даних.
Освіта
У навчальних закладах рішення двофакторної автентифікації та OTP токени набули широкого застосування. Ці інструменти відіграють важливу роль у захисті великої кількості конфіденційної інформації, яка стосується студентів та працівників. Використання 2FA в університетах, коледжах та школах є бар'єром проти несанкціонованого доступу, що забезпечує захист цінної освітньої інформації.
Охорона здоров'я
У сфері охорони здоров'я, де захист даних пацієнтів має вирішальне значення, використання 2FA є важливим елементом. Це не лише допомагає відповідати вимогам таких стандартів, як HIPAA, PCI DSS, HITRUST, Joint Commission та NIST, але й забезпечує безпечний доступ до даних пацієнтів та співробітників лікарень. Також використання апаратних токенів Protectimus для електронної перевірки візитів (Electronic Visit Verification, EVV) гарантує надійний захист від можливих порушень у сфері надання послуг по догляду за пацієнтами вдома.
Онлайн-ігри та азартні ігри
Для платформ для онлайн-ігр, азартних ігр та спортивних ставок двофакторна автентифікація є основним засобом захисту від шахрайства та використання викрадених облікових даних. Регулювання азартних ігор онлайн у більшості штатів вимагає від ігрових платформ впровадження багатофакторної автентифікації для своїх користувачів. Захищаючи облікові записи користувачів за допомогою 2FA, ці платформи забезпечують безпечніше середовище для користувачів, запобігаючи несанкціонованому доступу та шахрайським діям.
Технології та енергетика
У різних технологічних сферах компанії використовують багатофакторну автентифікацію для зміцнення своєї кібербезпеки. Технологія 2FA широко застосовується для захисту конфіденційних проєктів, фінансових систем, логістичних операцій і даних працівників. Вона забезпечує безпечний доступ до кінцевих пристроїв користувачів і допомагає запобігти порушенням безпеки в умовах постійних змін у технологічному середовищі.
Державні органи
У державних органах впровадження ініціатив з модернізації ІТ вимагає рішення з безпеки, яке здатне йти в ногу з часом. Технологія багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA) стає важливим елементом, забезпечуючи баланс між надійною безпекою та зручністю використання. Оскільки федеральні агентства впроваджують політику нульової довіри, технологія 2FA допомагає захистити доступ для мільйонів кінцевих користувачів, забезпечуючи надійний захист від потенційних загроз.
10. Поширені запитання про двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA)
1. Де можна увімкнути двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA)?
- Облікові записи електронної пошти: Додайте додатковий рівень захисту до своїх облікових записів електронної пошти за допомогою 2FA. Це дуже важливо, оскільки зламаний email може стати відчиненими дверима для хакерів, які отримають доступ до інших ваших акаунтів.
- Фінансові послуги: Посильте безпеку вашого онлайн-банкінгу, платіжних систем, криптовалютних бірж та інших фінансових акаунтів, активувавши 2FA.
- Акаунти, що містять платіжні дані: Посиліть безпеку акаунтів, в яких зберігаються ваші платіжні дані, таких як eBay та Amazon, активувавши 2FA. Це додає додатковий рівень захисту вашої фінансової інформації.
- Соціальні мережі: Захистіть свої акаунти у соціальних мережах, таких як Facebook та Instagram, активувавши 2FA. Це допоможе знизити ризик несанкціонованого доступу та можливого зловживання вашою особистою інформацією.
- Акаунти з особистими даними: Налаштуйте 2FA на акаунтах, що містять особисту інформацію, таких як myGov, щоб запобігти несанкціонованому доступу та забезпечити захист конфіденційних даних.
- Геймерські платформи: Оскільки платформи для онлайн ігор збирають особисті та фінансові дані для віддаленої перевірки особи та покупок ігор, доцільно захищати доступ до акаунтів на платформах, таких як Steam, Epic Games та PlayStation, за допомогою двофакторної автентифікації.
Процес налаштування двофакторної автентифікації може змінюватися залежно від конкретного програмного забезпечення або сервісу. Однак загальні кроки залишаються однаковими для більшості платформ. Захистіть свої онлайн-акаунти, увімкнувши 2FA на цих важливих сервісах.
2. Хто має використовувати двофакторну автентифікацію?
Двофакторна автентифікація (2FA) є важливою мірою безпеки для кожного, незалежно від рівня його онлайн-активності. Вона є необхідною для тих, хто ставить на перше місце надійний захист особистих і бізнес даних.
Ось кілька груп, яким слід впровадити двофакторну автентифікацію:
- Всі, хто має онлайн-акаунти. Особи, які користуються акаунтами на різних онлайн-платформах, включаючи електронну пошту, соціальні мережі, банківські послуги та сайти для покупок, повинні увімкнути 2FA. Це стосується як особистих, так і професійних акаунтів.
- Бізнеси та співробітники. Бізнеси повинні впроваджувати 2FA для своїх співробітників, щоб зміцнити безпеку корпоративних акаунтів та конфіденційної інформації. Це особливо важливо для доступу до корпоративної електронної пошти, інструментів для управління проєктами, акаунтів адміністраторів та інших бізнес-платформ.
- Співробітники, що працюють віддалено. В епоху віддаленої роботи бізнеси повинні обов'язково впроваджувати 2FA для працівників, які працюють з дому або з інших локацій, особливо при використанні VPN, RDP або VDI сервісів.
- Фінансові рахунки. Оскільки банківські та фінансові акаунти є привабливою мішенню для хакерів, тут впровадження 2FA є обов'язковим. Як для окремих осіб, так і для фінансових установ, що надають такі послуги, важливо забезпечити захист користувачів та співробітників за допомогою багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA).
- Користувачі соціальних мереж. Акаунти в соціальних мережах, що містять особисту інформацію, часто є мішенню для кіберзлочинців. Активація 2FA на таких платформах, як Facebook, Twitter і Instagram, є важливою для запобігання несанкціонованому доступу.
- Електронна пошта. Оскільки електронна пошта є дверима до багатьох інших онлайн-акаунтів (запити на скидання пароля, відновлення акаунта тощо), захист вашої пошти за допомогою 2FA є критично важливим. 2FA додає додатковий бар'єр проти несанкціонованого доступу до всього вашого онлайн-простору.
- Студенти та освітні установи. Студенти та користувачі освітніх платформ або систем управління навчанням повинні впровадити 2FA для захисту академічної та особистої інформації. Освітні установи повинні підтримувати це, запровадивши двофакторну автентифікацію.
- Охорона здоров'я та чутлива інформація. Особи, які мають акаунти з чутливою медичною або особистою інформацією, повинні першочергово впроваджувати 2FA для захисту конфіденційності та запобігання крадіжці особистих даних. Лікарні та медичні заклади повинні забезпечити впровадження 2FA для захисту даних пацієнтів.
- Користувачі криптовалют. Користувачі криптовалютних бірж та гаманців повинні активувати 2FA для захисту своїх цифрових активів. Біржі криптовалют повинні звернути увагу на це та забезпечити додатковий рівень захисту для своїх користувачів через підвищений ризик атак.
- Особи з цінними або конфіденційними даними. Кожен, хто зберігає цінні або конфіденційні дані в Інтернеті, такі як інтелектуальна власність, комерційна інформація чи конфіденційні документи, повинен використовувати 2FA для зменшення ризику несанкціонованого доступу.
На завершення, двофакторна автентифікація є універсальним і незамінним інструментом для підвищення безпеки в Інтернеті серед широкого кола користувачів і галузей.
3. Чи легко налаштувати двофакторну автентифікацію?
Так, двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA) зазвичай легко налаштувати, хоча процес може відрізнятися залежно сервісу, на якому ви налаштовуєте 2FA. У більшості випадків налаштування включає такі кроки:
- Увійдіть до свого облікового запису.
- Перейдіть до налаштувань безпеки або налаштувань облікового запису.
- Виберіть метод 2FA (MFA застосунок, апаратний токен, SMS, email, 2FA-бот).
- Дотримуйтесь інструкцій на екрані (скануйте QR-код або введіть ключ налаштування).
- Підтвердьте налаштування за допомогою одноразового пароля.
- Збережіть резервні коди або налаштуйте варіанти відновлення доступу.
Завжди дотримуйтеся інструкцій платформи чи сервісу, на якому ви налаштовуєте багатофакторну автентифікацію. 2FA додасть додатковий рівень захисту вашим акаунтам.
4. Наскільки ефективна двофакторна автентифікація у підвищенні безпеки?
Двофакторна автентифікація (2FA) є дуже ефективним способом підвищення безпеки. Вона додає додатковий рівень захисту до вашого пароля, що значно ускладнює несанкціонований доступ до ваших акаунтів Ось кілька основних причин, чому 2FA така ефективна:
- Зменшує наслідки викрадених паролів та їх слабкості: Навіть якщо ваш пароль слабкий або стався витік даних чи фішингова атака, викрадених паролів буде недостатньо для доступу без другого фактора автентифікації.
- Захищає від несанкціонованого доступу: 2FA перешкоджає несанкціонованому входу, навіть якщо хтось має ваш пароль або намагається увійти з іншого місця.
- Тимчасові коди: Додатки для аутентифікації створюють коди, які діють лише протягом обмеженого часу, що підвищує рівень безпеки, обмежуючи можливість їх використання.
- Різноманітні методи аутентифікації: Підтримка SMS, додатків для аутентифікації, електронної пошти, чат-ботів або апаратних токенів OTP дозволяє користувачам вибирати метод відповідно до їхніх уподобань і потреб безпеки.
- Відповідність стандартам і найкращим практикам: 2FA рекомендовано стандартами безпеки і є основним методом захисту чутливої інформації.
Однак 2FA не є абсолютним захистом. Користувачі повинні дотримуватись основних правил безпеки, уникати фішингу та вибирати надійний другий фактор, наприклад, додаток для автентифікації з хмарним резервним копіюванням або апаратний токен 2FA для додаткової надійності. Загалом, 2FA залишається важливим і ефективним інструментом для підвищення онлайн-безпеки.
Поглибте свої знання про багатофакторну автентифікацію, ознайомившись з матеріалом 6 міфів про MFA, в які ви досі вірите.
5. Чи можу я використовувати двофакторну автентифікацію без смартфона?
Так, ви можете використовувати двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA) без смартфона. Хоча багато методів 2FA передбачають використання мобільних додатків, існують альтернативні варіанти, які не потребують смартфона:
- Апаратні OTP токени: Деякі сервіси пропонують апаратні токени або брелоки, які генерують одноразові коди і використовуються як другий фактор автентифікації. Якщо ж ваш сервіс не підтримує такі токени, ви все одно можете використовувати програмовані токени, як-от Protectimus Flex або Protectimus Slim, на таких вебсайтах. Зверніть увагу, що для їх налаштування потрібен смартфон на Android. Після програмування смартфон більше не буде потрібний.
- Текстові повідомлення (SMS): Популярний метод, що полягає в отриманні коду підтвердження через SMS. Код надсилається на ваш зареєстрований номер мобільного телефону, і ви вводите його під час входу в систему.
- Перевірка через телефонний дзвінок: Деякі сервіси пропонують 2FA через перевірку за допомогою телефонного дзвінка. Ви отримуєте автоматичний дзвінок, який повідомляє код підтвердження, який потрібно ввести.
- Перевірка через електронну пошту: Інший варіант — отримати код підтвердження через електронну пошту. Цей код надсилається на вашу зареєстровану електронну адресу, і ви використовуєте його для завершення процесу автентифікації.
- Резервні коди: Деякі платформи пропонують резервні коди, які можна згенерувати і зберігати в безпечному місці. Ці коди служать резервним варіантом, якщо ви не можете отримати коди через основний метод 2FA.
Розширте своє розуміння методів доставки та генерації одноразових паролів, ознайомившись з нашим докладним матеріалом Переваги та недоліки різних типів і методів двофакторної автентифікації.
6. Що робити, якщо я втрачу доступ до пристрою для двофакторної автентифікації?
Якщо ви втрачаєте доступ до пристрою для двофакторної автентифікації (2FA), виконайте наступні кроки:
- Використайте хмарну резервну копію (якщо застосовно): Якщо ви використовуєте додаток 2FA, наприклад, Protectimus Smart з активованим хмарним бекапом, ви зможете легко відновити свої токени і повернути доступ до акаунтів.
- Використовуйте резервні коди: Перевірте наявність резервних кодів, наданих під час налаштування, і використовуйте їх для входу.
- Спробуйте альтернативні методи 2FA: Перевірте, чи пропонує сервіс альтернативні методи (наприклад, SMS, електронну пошту або телефонний дзвінок) і скористайтеся ними.
- Дослідіть варіанти відновлення акаунту: Багато сервісів надають можливість відновлення акаунту. Підтвердіть свою особу іншим доступним способом або дотримуйтесь вказаного сервісом процесу відновлення акаунту.
- Зверніться до служби підтримки: Якщо не вдалося відновити доступ, зверніться до служби підтримки для отримання допомоги.
Щоб уникнути проблем у майбутньому:
- Використовуйте надійний застосунок для 2FA: Використовуйте застосунок для двофакторної автентифікації з зашифрованою хмарною резервною копією для легкого відновлення на новому пристрої.
- Зберігайте резервні коди: Надійно зберігайте всі резервні коди, надані під час налаштування 2FA.
- Налаштуйте кілька методів 2FA: Використовуйте різні способи двофакторної автентифікації, щоб мати запасний варіант доступу.
- Оновлюйте контактні дані: Переконайтеся, що ваша електронна пошта та номер телефону для відновлення доступу завжди актуальні.
7. Чи можна зламати двофакторну автентифікацію?
Двофакторна автентифікація (2FA) значно підвищує рівень безпеки, але не є абсолютно захищеною від злому. Існують способи обходу 2FA, проте вони зазвичай потребують складніших методів, ніж проста крадіжка пароля. Ось деякі потенційні загрози:
- Фішингові атаки в реальному часі: Зловмисники можуть використовувати фішинг, щоб обманом змусити користувача ввести як пароль, так і другий фактор автентифікації. Це може відбуватися через підроблені сайти або шкідливі електронні листи.
- Атаки «людина посередині» (Man-in-the-Middle): Зловмисник може перехопити та змінити дані, що передаються між користувачем і сервісом, отримавши як пароль, так і код 2FA.
- Перехоплення номера (SIM Swapping): Якщо зловмисник переконає вашого мобільного оператора перенести номер на іншу SIM-карту, він зможе отримувати 2FA-коди, надіслані через SMS.
- Кейлогери: Шкідливе програмне забезпечення або кейлогер на вашому пристрої можуть перехоплювати як пароль, так і 2FA-код під час їх введення.
- Атака методом підбору (Credential Stuffing): Якщо зловмисник отримав список скомпрометованих паролів, він може спробувати використати їх разом із перехопленими 2FA-кодами на інших сервісах.
- Соціальна інженерія: Зловмисники можуть обманом змусити користувачів або службу підтримки надати доступ чи скинути налаштування 2FA.
Хоча існують певні ризики, впровадження двофакторної автентифікації (2FA) значно підвищує рівень захисту і ускладнює злом для зловмисників. Для максимізації ефективності 2FA важливо використовувати кілька різних методів автентифікації. Крім того, користувачі повинні уникати передачі кодів, бути обережними з підозрілими посиланнями, регулярно оновлювати програмне забезпечення та системи, а також залишатися пильними щодо фішингових атак.
Для додаткового захисту користувачі можуть вжити проактивних заходів, таких як впровадження підпису даних і CWYS (Confirm What You See) для боротьби з фішингом. Більш надійні методи, такі як апаратні токени, забезпечують підвищений рівень безпеки порівняно з використанням лише SMS. Для зміцнення загальної безпеки важливо застосовувати 2FA для кожного акаунта, використовувати надійні паролі та уникати входів через сторонні сервіси.
Хоча жоден захід безпеки не є абсолютно непроникним, очевидно, що використання 2FA залишається найкращою практикою для покращення онлайн-безпеки.
Заглибтеся в тонкощі цієї теми, прочитавши статтю "Уразливості 2FA, про які вам слід знати".
8. У чому різниця між MFA та двофакторною автентифікацією (2FA)?
Хоча 2FA та MFA можуть здаватися взаємозамінними термінами, між ними є певна різниця. Двофакторна автентифікація (2FA) передбачає використання двох факторів для автентифікації користувача — зазвичай це пароль і другий фактор, наприклад, OTP або push-сповіщення. Натомість багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA) є більш загальним поняттям і охоплює використання двох або більше факторів для автентифікації користувача. MFA виходить за межі 2FA, включаючи різні методи, такі як біометрія, фільтри за місцем і часом, або смарт-карти, крім традиційних факторів, як паролі та OTP. Таким чином, 2FA є підкатегорією MFA, підкреслюючи, що MFA пропонує більш широкий вибір методів автентифікації, забезпечуючи більшу гнучкість і рівень безпеки порівняно з двома факторами.
11. Інструкції для користувачів Protectimus
1. Покрокова інструкція з налаштування Protectimus MFA
Налаштування багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA) Protectimus та її інтеграція в інфраструктуру складаються з кількох простих етапів. Важливо зазначити, що конкретний процес може дещо відрізнятися в залежності від сервісу, який ви захищаєте, та від того, чи обираєте ви хмарний сервіс MFA, чи локальну платформу MFA Protectimus.
Рекомендуємо почати тестування системи двофакторної автентифікації Protectimus, налаштувавши хмарний сервіс. Перехід між хмарними та локальними серверами автентифікації простий і потребує лише незначних змін в конфігураційному файлі.
Для початку роботи з хмарним сервісом MFA Protectimus:
- Створіть обліковий запис Protectimus:
Перейдіть на SAAS сервіс Protectimus та зареєструйте обліковий запис. - Перейдіть до панелі керування:
Увійдіть у свій обліковий запис Protectimus і перейдіть до панелі керування. - Додайте ресурс:
Перейдіть до розділу «Ресурси» та натисніть «Додати ресурс». Введіть назву ресурсу на ваш вибір; інші параметри є необов'язковими. - Інтегруйте хмарний сервіс багатофакторної автентифікації Protectimus з вашою системою:
Процес інтеграції може відрізнятися в залежності від системи, яку ви захищаєте. Доступ до інструкцій по інтеграції для різних систем можна знайти на сторінці документації.
2. Які методи аутентифікації підтримує Protectimus?
Protectimus пропонує різноманітні методи аутентифікації, які відповідають стандарту OATH і покликані задовольнити різні потреби в безпеці. Кожен метод розроблений для конкретних завдань, забезпечуючи комплексний і гнучкий підхід до багатофакторної аутентифікації для особистих і корпоративних потреб.
АПАРАТНІ TOTP ТОКЕНИ
- OTP токени з можливістю програмування, що є апаратною альтернативою застосункам для 2FA.
- Доступні у стандартному вигляді банківської картки та міні-форматі.
- Підтримує алгоритми TOTP (RFC 6238) з підтримкою SHA-1.
- Ідеально підходить для корпоративного використання з Google Authenticator, Microsoft Azure MFA, а також для особистого використання на різних платформах.

- Надійні водостійкі апаратні OTP токени з високим рівнем захисту.
- Використовує TOTP алгоритм з підтримкою SHA-1.
- Ідеально підходить для корпоративного використання з сервісом Protectimus MFA та іншими MFA системами, якщо у вас є можливість додати секретні ключі до цієї системи.

- Програмований апаратний TOTP токен у форматі брелока.
- Підтримує алгоритми TOTP (RFC 6238) з SHA-1.
- Підходить як для корпоративного, так і для особистого використання в різних сервісах автентифікації.

- Класичний апаратний TOTP токен з підтримкою алгоритму SHA-256.
- Має LED-дисплей з шістьма цифрами та індикатором часу.
- Підходить для корпоративного використання з MFA сервісом Protectimus та іншими MFA системами, якщо у вас є можливість додати секретні ключі до цієї системи.

2FA ЗАСТОСУНОК PROTECTIMUS SMART
2FA застосунок Protectimus SMART
- Безкоштовний застосунок для 2FA на iOS та Android.
- Зашифроване хмарне резервне копіювання, захист PIN-кодом та біометричний захист.
- Підтримує різні алгоритми, зашифрований хмарний бекап та налаштовування довжини OTP.
- Ідеально підходить для особистого використання на будь-якому вебсайті, що підтримує 2FA, та для корпоративного використання з Protectimus або іншими сервісами автентифікації.
БЕЗКОШТОВНІ МЕТОДИ ДОСТАВКИ OTP
- Безкоштовна доставка OTP за допомогою чат-ботів у месенджерах, що є надійною альтернативою SMS.
- Підтримує алгоритми HOTP та OCRA, а також функцію підпису даних.
- Підходить для корпоративного використання з MFA-сервісом Protectimus.
- Безкоштовна доставка одноразових паролів через електронну пошту з алгоритмами HOTP та підписом даних.
- Підходить для корпоративного використання з MFA-сервісом Protectimus.
- Доставка одноразових паролів черезSMS-повідомлення.
- Підтримує алгоритми HOTP та підпис даних.
- Підходить для корпоративного використання з MFA-сервісом Protectimus.
3. Чи можна використовувати Protectimus як для особистих, так і бізнес-акаунтів?
Звісно! Protectimus пропонує рішення для обох категорій — як для особистих, так і для бізнес-акаунтів. Ви можете скористатися різними компонентами для інтеграції та методами 2FA, такими як апаратні токени, мобільні додатки та сервіси доставки OTP. Це дає можливість вибрати найбільш зручний і підходящий варіант для кожної ситуації. Хоча багато продуктів Protectimus орієнтовані на бізнес, також є чудові рішення для особистого використання.
Для особистого використання ідеально підходить безкоштовний 2FA додаток Protectimus SMART OTP, що підтримує можливість створення зашифрованої хмарної резервної копії. Це чудовий вибір для захисту особистих акаунтів на сайтах, які підтримують двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA). Також програмовані апаратні токени Protectimus Slim і Protectimus Flex чудово підходять як для особистого, так і для бізнес-використання. Вони легко підключаються до майже будь-якої платформи, такої як Google, Dropbox, GitHub, Microsoft, Facebook і багатьої криптовалютних бірж, і можуть бути використані як альтернатива застосункам для генерації одноразових паролів.
Крім того, Protectimus пропонує просте рішення двофакторної автентифікації для Windows та RDP. Воно легко встановлюється і підтримує до 10 користувачів безкоштовно. Це рішення стане в нагоді як для бізнесів, так і для осіб, які бажають покращити безпеку своїх особистих акаунтів Windows.
Для бізнес-сфери Protectimus пропонує надійну платформу багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA) з різноманітними варіантами апаратних і програмних рішень. Це забезпечує комплексний підхід до захисту корпоративних систем і додатків.
4. Чи відповідає Protectimus вимогам галузевих стандартів безпеки?
Protectimus відповідає галузевим стандартам безпеки завдяки сертифікаціям, що підтверджують ефективність цих рішень для багатофакторної автентифікації. Одне з таких визнань — це сертифікація OATH від ініціативи Open Authentication. OATH — це провідна організація, що підтримує надійну автентифікацію та проводить програму сертифікації. Вона ретельно перевіряє та сертифікує продукти постачальників MFA, щоб переконатися, що вони відповідають вимогам, зазначеним у профілях сертифікації OATH.
Крім того, Protectimus має сертифікацію Citrix Ready Partner, що підтверджує сумісність цього рішення для двофакторної автентифікації з продуктами Citrix. Це визнання було надано після оцінки експертами Citrix, що підтвердили надійність та сумісність рішення Protectimus для інтеграції з продуктами Citrix. Як партнер Citrix Ready, Protectimus отримав офіційну рекомендацію для безперешкодного використання з продуктами Citrix.

5. Як налаштувати Protectimus для різних додатків та акаунтів?
Налаштування Protectimus для різних додатків та акаунтів — це просто:
Простота інтеграції в будь-яку інфраструктуру: Protectimus спрощує процес інтеграції завдяки різноманітним плагінам для MFA, що дозволяє швидко налаштувати багатофакторну автентифікацію для всіх систем у вашій інфраструктурі. Крім того, Protectimus пропонує зручний API, доступний навіть в безкоштовному тарифному плані, що робить інтеграцію гнучкою. Розробники також можуть скористатися наборами для розробки програмного забезпечення (SDK) на популярних мовах, таких як Java, PHP та Python. Якщо необхідний плагін відсутній, спеціалізована команда розробників готова допомогти у підключенні та інтеграції з будь-яким сервісом.
Зручне групування та управління користувачами: Protectimus спрощує управління користувачами через використання ресурсів. В одному обліковому записі можна створювати кілька ресурсів, кожен з яких має окремих адміністраторів. Наприклад, вимоги до захисту для кінцевих користувачів і адміністраторів можуть бути різними. Один ресурс можна налаштувати для кінцевих користувачів, пропонуючи різні варіанти токенів, як-от апаратні токени, додатки для 2FA або підключення до чат-бота Protectimus у месенджерах. Інший ресурс в тому ж обліковому записі буде призначений для адміністраторів, розробників і технічної підтримки, де застосовуються більш суворі вимоги до автентифікації, зокрема використання лише апаратних токенів і фільтрація за часом та місцем. Такий підхід дозволяє ефективно управляти різними групами користувачів, кожна з яких має свої специфічні вимоги до безпеки залежно від рівня доступу до чутливих даних.
6. Які варіанти підтримки доступні, якщо виникають проблеми з Protectimus?
Ми розуміємо, наскільки важлива своєчасна допомога, тому наші послуги підтримки спрямовані на те, щоб задовольнити ваші потреби.
Підтримка 8/5
Наша команда готова допомогти вам протягом робочих годин у будні дні, надаючи підтримку для всіх платних тарифних планів (Starter, Business, Custom, Platform, Cluster) без додаткових оплат. Ви можете звернутися до нас по електронній пошті за адресою support@protectimus.com, телефоном або скористатися контактною формою на нашому вебсайті. Крім того, система підтримки в панелі управління Protectimus Platform забезпечує швидку та організовану відповідь.
Розширені опції підтримки (за додаткову плату)
Для тих, хто потребує додаткової підтримки, ми пропонуємо розширені варіанти обслуговування:
- Підтримка 24/5: Підтримка доступна 24 години на добу, п’ять днів на тиждень.
- Підтримка 24/7: Оформіть цілодобову підтримку, сім днів на тиждень.
З нашою розширеною підтримкою ви також отримуєте доступ до екстреного номера для негайної допомоги в критичних ситуаціях. Це гарантує, що ви отримаєте рівень підтримки, який відповідає вашим конкретним потребам.
7. Чи сумісний Protectimus з популярними платформами та сервісами?
Звісно! Рішення для багатофакторної автентифікації (MFA) від Protectimus сумісне з різноманітними популярними платформами та сервісами. Ми пропонуємо плагіни для легкого підключення та можливість безперешкодної інтеграції 2FA через API. Легко інтегруючись з різними системами та додатками, продукти Protectimus забезпечують надійний захист даних на таких платформах, як MacOS, Windows (локально та через віддалений доступ через RDP), Ubuntu, OWA, ADFS, Active Directory, LDAP, Roundcube та системи, що підтримують протокол RADIUS. Якщо у вас виникнуть питання або проблеми, наша команда розробників завжди готова допомогти.
8. Як довго працюють токени Protectimus і як їх замінити?
Апаратні OTP токени Protectimus зазвичай мають термін служби, який покривається гарантією 12 місяців і 2 тижні з дати відправлення. Гарантія діє за умови нормальних експлуатаційних умов і відсутності механічних пошкоджень. Зазвичай ці токени служать від 3 до 5 років, залежно від часу роботи батареї та кількості генерованих OTP. Зверніть увагу, що якщо токени працюють належним чином, повернення або обмін неможливі. Апаратні токени розроблені для інформаційної безпеки та містять конфіденційні вбудовані секретні ключі, які не можна передавати іншому клієнту.
9. Як відновити доступ до мого облікового запису, якщо я втрачу смартфон або токен Protectimus?
Якщо ви втратили смартфон з додатком для генерації одноразових паролів або токен Protectimus, зверніться до вашого адміністратора для отримання допомоги.
Якщо ви є адміністратором і втратили доступ до свого облікового запису Protectimus, будь ласка, зв'яжіться з нашою службою підтримки для подальшої допомоги.
- 1. Що таке багатофакторна автентифікація (MFA)?
- 2. Фактори багатофакторної автентифікації
- 3. Як працює багатофакторна автентифікація
- Розбір процесу багатофакторної автентифікації:
- 4. Значення багатофакторної автентифікації
- 5. Від яких загроз захищає багатофакторна автентифікація
- Фішинг
- Брутфорс
- Використання кейлогерів
- Використання крадених облікових даних
- Перехоплення сеансу
- Соціальна інженерія
- Атаки типу "Людина посередині"
- Скомпрометовані паролі
- 6. Приклади багатофакторної автентифікації
- Різні правила безпеки для груп користувачів у Volet
- Корпоративна безпека в Xchanging Italy
- Захист доступу до VPN та email в SICIM
- 7. Методи багатофакторної автентифікації
- Автентифікація на основі знань
- Аппаратні OTP-токени
- SMS-автентифікація
- Застосунки для двофакторної автентифікації
- Автентифікація через чат-боти в месенджерах
- Push-сповіщення для 2FA
- Email-автентифікація
- Біометрична автентифікація
- Аутентифікація на основі місцезнаходження та часу
- 8. Впровадження багатофакторної автентифікації в організаціях
- 9. Які галузі використовують багатофакторну автентифікацію
- Фінансові послуги
- Освіта
- Охорона здоров'я
- Онлайн-ігри та азартні ігри
- Технології та енергетика
- Державні органи
- 10. Поширені запитання про двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA)
- 1. Де можна увімкнути двофакторну автентифікацію (2FA)?
- 3. Чи легко налаштувати двофакторну автентифікацію?
- 4. Наскільки ефективна двофакторна автентифікація у підвищенні безпеки?
- 5. Чи можу я використовувати двофакторну автентифікацію без смартфона?
- 6. Що робити, якщо я втрачу доступ до пристрою для двофакторної автентифікації?
- 7. Чи можна зламати двофакторну автентифікацію?
- 8. У чому різниця між MFA та двофакторною автентифікацією (2FA)?
- 11. Інструкції для користувачів Protectimus
- 1. Покрокова інструкція з налаштування Protectimus MFA
- 2. Які методи аутентифікації підтримує Protectimus?
- 3. Чи можна використовувати Protectimus як для особистих, так і бізнес-акаунтів?
- 4. Чи відповідає Protectimus вимогам галузевих стандартів безпеки?
- 5. Як налаштувати Protectimus для різних додатків та акаунтів?
- 6. Які варіанти підтримки доступні, якщо виникають проблеми з Protectimus?
- 7. Чи сумісний Protectimus з популярними платформами та сервісами?
- 8. Як довго працюють токени Protectimus і як їх замінити?
- 9. Як відновити доступ до мого облікового запису, якщо я втрачу смартфон або токен Protectimus?


